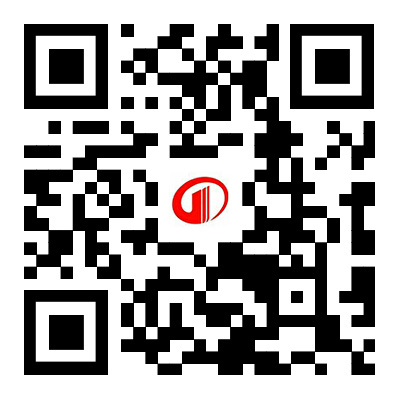
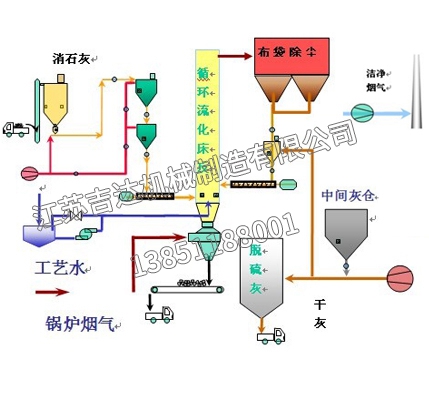
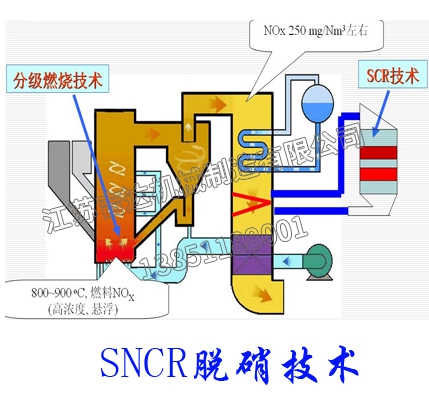
The SNCR-SCR combined denitrification technology uses SNCR technology to inject reducing agents such as ammonia and urea solution into the furnace temperature range of 850-1100 ℃ for denitrification reaction. Excess ammonia can be decomposed into N2 and H2O in the flue gas temperature range of 280-420 ℃ under the action of the catalyst. The combined denitrification system combines the advantages of two technologies, which can reduce denitrification costs and minimize ammonia leakage while improving the removal rate of NOX. In the joint denitrification system, the ammonia leakage during the SNCR process provides the required reducing agent for SCR. The SCR denitrification process can remove more NOx and further reduce the chance of ammonia leakage. The catalyst used in the combined denitrification system is much less than that used in the SCR denitrification system alone, and can achieve a higher NOx removal rate.
The SCR/SNCR combined removal technology is an emerging development in dry flue gas denitrification technology. It is a new process that combines the high efficiency of selective catalytic reduction flue gas denitrification technology (SCR) and the low investment of selective non catalytic reduction flue gas denitrification technology (SNCR).
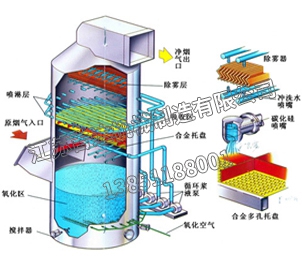
Selective catalytic reduction denitrification technology refers to the selective reaction of reducing agents (NH3, urea) with NOx under the action of metal catalysts to generate N2 and H2O, rather than being oxidized by O2, hence it is called "selective". NH3, CO, H2, as well as methane, ethylene, propane, propylene, and others can be used as reducing agents for SCR reactions.
Selective non catalytic reduction denitrification technology does not require a catalyst, and the selected reducing agent is the same as SCR, which is NH3, ammonia water, or urea. SNCR sprays reducing agents above the boiler and into the horizontal flue, selectively reacting with NOx in the flue gas to produce harmless N2 and H2O.
The advantage of the former is that the denitrification rate can be greater than 80% and the NH3 consumption is more optimized, while the disadvantage is that it requires higher design requirements; The design is quite complex; The manufacturing and operating costs are relatively high. The advantage of the latter is that the investment cost for retrofitting is relatively low, making it more suitable for SNCR retrofitting of existing boilers. The disadvantage is that the ammonia consumption is high; The amount of ammonia escaping is relatively large; The difficulty of mixing evenly is high; So its denitrification rate is relatively low, only 50-60%.
The SNCR/SCR mixed flue gas denitrification technology combines the reducing agent injection technology of SNCR process into the furnace with the catalytic reaction technology of SCR process using escaping ammonia to further remove NOx. The "joint process" was first tested on a fuel plant in Japan in the 1970s, and the experiment demonstrated the feasibility of the technology. In recent years, with the development of chimney denitrification technology, many new chimney denitrification technologies have been applied to production and have achieved very good results. At the same time, chimney flue gas denitrification technology has been continuously optimized in the reform, and its performance and effectiveness have also been continuously improved in this reform. Therefore, many new chimney flue gas denitrification technologies have been officially used as technical projects in production. It effectively combines the SNCR process and SCR, while maintaining and promoting the advantages of both processes, utilizing each other's strengths to suppress and overcome the drawbacks of high cost and low efficiency of a single SCR. SNCR and SCR complement each other, complement each other's strengths and weaknesses, and complement each other.