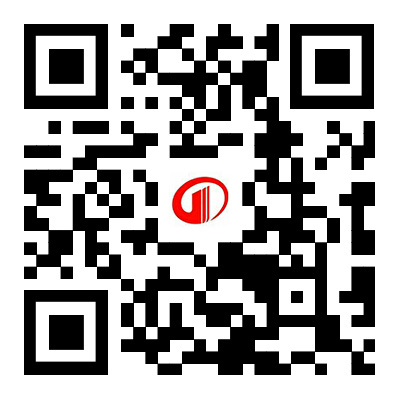
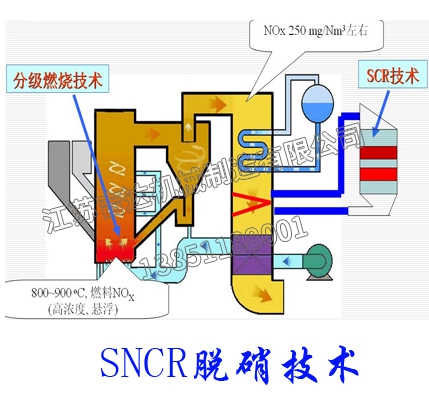
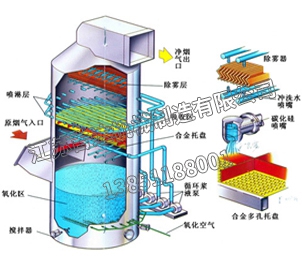
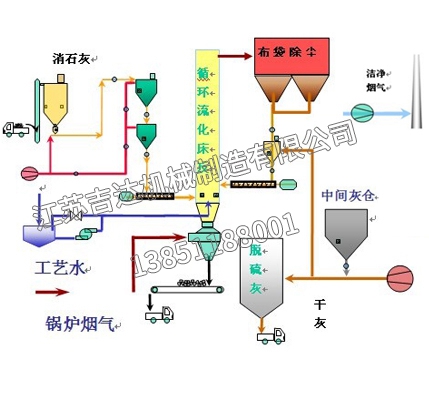
Selective Non Catalytic Reduction (SNCR) technology is a mature commercial NOx control and treatment technology. The SNCR method mainly sprays nitrogen-containing chemicals into lean flue gas at 850-1100 ℃ to reduce NO and generate nitrogen and water. And selective catalytic reduction (SCR), due to the use of catalysts, can remove NOx at temperatures of 300-400 ℃. Both methods utilize the selectivity of reducing agents for NOx reduction, effectively avoiding the reaction between reducing agents and a large amount of oxygen in lean flue gas, hence they are called selective reduction methods. The chemical reaction principles of the two methods are the same. But the investment in SCR technology system is relatively large.
The SNCR denitrification method involves injecting reducing agent ammonia or urea into the furnace in the absence of a catalyst to reduce NOx to N2 and H2O. The reducing agent is sprayed into the furnace (850 ℃~1000 ℃), with a denitrification efficiency of 30%~60%. Within the temperature range of around 950 ℃, the reaction equation is:
4NH3+4NO+O2→4N2+6H2O
When the temperature is too high, the following side reactions will occur, which will also generate NO:
4NH3+5O2→4NO+6H2O
Compared with other denitrification technologies, SNCR technology has the following advantages:
☆The denitrification effect is satisfactory: SNCR technology is applied to CFB boilers, and long-term on-site application can generally achieve a NOx removal rate of 30-70%.
☆Reducing agents are diverse and readily available: In SNCR technology, the reducing agents used to remove NOx are generally nitrogen-containing substances, including ammonia, urea, cyanuric acid, and various ammonium salts (ammonium acetate, ammonium bicarbonate, ammonium chloride, ammonium oxalate, ammonium citrate, etc.). But the most effective and widely used in practical applications are ammonia and urea.
☆No secondary pollution: SNCR technology is a clean technology that generates no solid or liquid pollutants or by-products, and has no secondary pollution.
☆Good economy: As the reaction of SNCR is driven by high temperature inside the boiler, it does not require expensive catalyst systems, resulting in lower investment and operating costs.
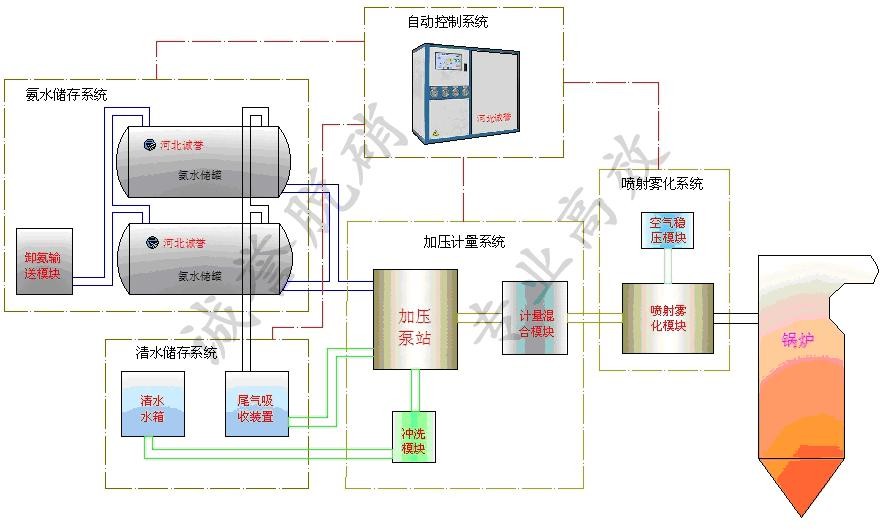
☆Simple system and short construction time: The main system of SNCR technology is the storage system and injection system for reducing agents, with main equipment including storage tanks, pumps, spray guns, necessary pipelines, and measurement and control equipment. Due to the simplicity of the equipment and the short installation period of SNCR technology, it only takes about 2 days to shut down the furnace, and the furnace construction can be completed during minor repairs.
☆Easy to operate: SNCR technology does not require modifications to the boiler, nor does it require changes to the normal operation mode of the boiler, and it will not have a significant impact on the main operating parameters of the boiler.