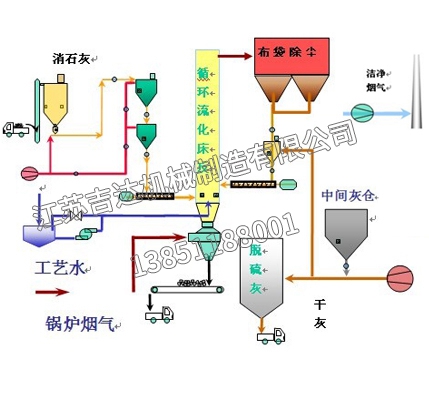
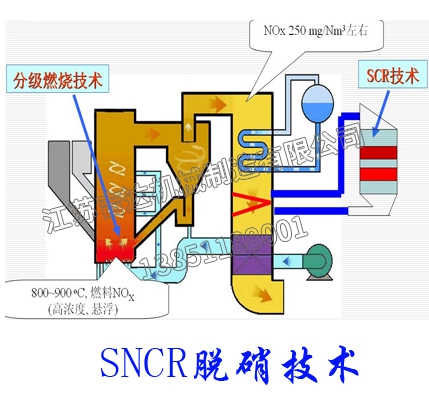
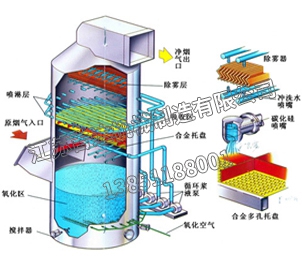
Dry flue gas desulfurization refers to the use of powdered or granular absorbents, adsorbents, or catalysts to remove SO2 from flue gas. Definition of dry flue gas desulfurization: CaCO3 injected into the furnace is calcined at high temperature and decomposed into CaO, which reacts with SO2 in the flue gas to produce calcium sulfate; The use of electron beam irradiation or activated carbon adsorption to convert SO2 into ammonium sulfate or sulfuric acid is collectively referred to as dry flue gas desulfurization technology.
Its advantages are simple process, no sewage or acid treatment problems, low energy consumption, especially the high temperature of purified flue gas, which is conducive to chimney exhaust diffusion and does not produce "white smoke" phenomenon. The purified flue gas does not require secondary heating and has low corrosiveness; Its disadvantages are low desulfurization efficiency, large equipment, high investment, large footprint, and high operational technical requirements.
FEATURES
1)The integrated design of digestion with quicklime (CaO) and humidification with ash circulation ensures that high-quality quicklime (Ca (OH) 2) freshly digested is immediately put into the circulating desulfurization reaction;
2)Utilize circulating ash to carry moisture and form a water film on the surface of dust particles. The thin layer of water film on the surface of dust particles evaporates instantly in the flue gas flow, forming an ideal reaction environment with suitable temperature and humidity in a very short time. At the same time, it also overcomes the wall sticking problem that may occur in traditional semi dry desulfurization reactors;
3)Due to the reduced time required to establish an ideal reaction environment, it is possible to significantly reduce the total reaction time, which can effectively lower the height of the desulfurization reactor;
4)The flue gas flows at high speed in the reactor, and the entire device has a compact structure, small volume, and reliable operation. The device has good load adaptability;
5)The by-products of desulfurization are in a dry state, and the system produces no water. The final product has good mobility and is suitable for pneumatic conveying. After desulfurization, the flue gas can be directly discharged without the need for further heating;
6)The requirements for absorbents are not high and can be widely obtained.
7)By reducing the size and footprint of the absorption tower, as well as avoiding the use of complex and expensive digestion preparation systems, the initial investment and operating costs have been greatly reduced;
8)High desulfurization efficiency, with a desulfurization efficiency of over 90%.